Traumatic Eye Injuries: Causes, Symptoms, and Why Immediate Care Matters
Our eyes are among the most delicate and vital organs in the body, yet they are also vulnerable to accidents and injuries. Traumatic eye injuries can occur suddenly and with little warning, often leaving long-term consequences if not treated quickly. From a simple bruise to a severe orbital fracture, eye trauma should never be ignored. Understanding what causes these injuries, how to recognize the warning signs, and why immediate medical attention is crucial can help protect your vision for years to come.
What Is a Traumatic Eye Injury?
A traumatic eye injury refers to any damage caused to the eye or the tissues surrounding it by an external force. Unlike infections or chronic conditions, trauma usually results from a sudden incident such as a fall, a sports collision, a car accident, or direct impact from an object. The injury can range from mild swelling to severe internal bleeding and even vision loss.
Doctors categorize traumatic eye injuries into several types:
-
Blunt force trauma – when the eye is struck by a rounded or heavy object, such as a ball or fist.
-
Penetrating trauma – when a sharp object pierces the eye or surrounding tissue.
-
Chemical or thermal burns – when the eye comes into contact with harmful substances or extreme heat.
-
Orbital fractures – when the bones around the eye socket break due to strong impact.
Each type requires a different approach to diagnosis and treatment, but all share one common fact: immediate medical attention is essential.

Common Causes of Traumatic Eye Injuries
Eye trauma can happen to anyone, at any time, but certain situations carry higher risks. Some of the most common causes include:
-
Sports accidents – Fast-moving balls, elbows, or equipment in sports like basketball, soccer, or baseball often lead to blunt trauma.
-
Falls and daily accidents – Slips at home or workplace accidents can result in direct injury to the eye area.
-
Motor vehicle collisions – High-speed impacts frequently cause orbital fractures or serious bruising around the eyes.
-
Workplace hazards – Construction, manufacturing, and laboratory environments expose workers to risks from flying debris, chemicals, or sharp tools.
-
Assault or physical conflict – Unfortunately, physical altercations are another major source of eye injuries.
Even something as simple as not wearing protective eyewear during a risky activity can significantly increase the chance of trauma.
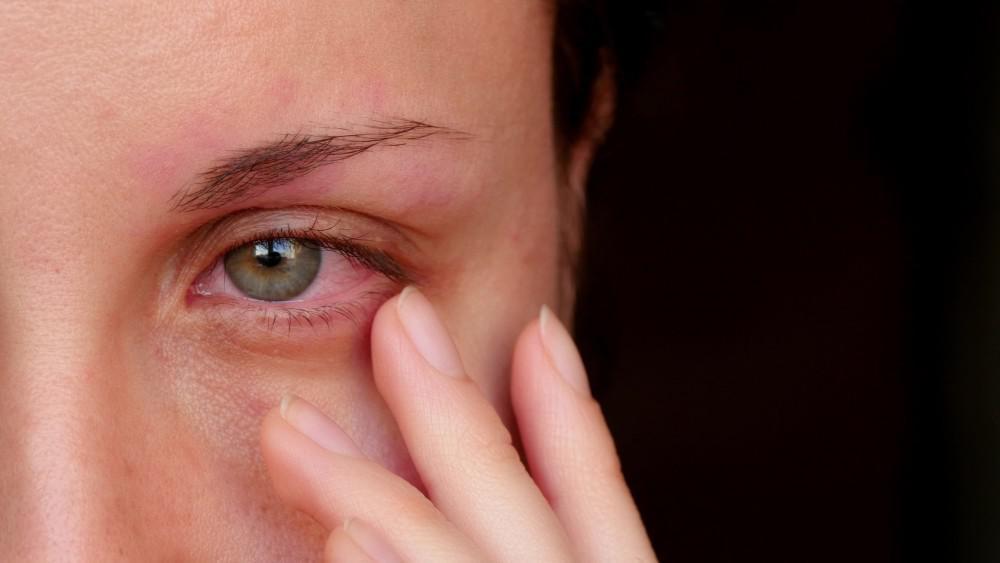

Recognizing the Symptoms
Eye injuries are not always immediately obvious, but certain warning signs should never be ignored. These include:
-
Swelling and bruising around the eyelid (commonly called a “black eye”).
-
Redness or bleeding inside the eye.
-
Blurred or double vision.
-
Pain or pressure around the eye socket.
-
Difficulty opening the eyelid due to swelling.
-
Sensitivity to light.
-
Loss of part or all of the visual field.
Severe symptoms, such as sudden vision loss, large amounts of blood inside the eye, or inability to move the eye properly, indicate an emergency and require urgent medical evaluation.

Why Immediate Care Is Crucial
The eye is an incredibly complex organ, and even minor injuries can lead to lasting damage if not managed correctly. Seeking professional care quickly can make the difference between a full recovery and permanent complications such as partial vision loss, glaucoma, or retinal detachment.
Doctors may use imaging tools like CT scans or ultrasounds to check for internal damage. In some cases, surgery may be required to repair torn tissues or fractures around the eye socket. Medications such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or special eye drops can also play a role in recovery.
Prevention: Protecting Your Eyes from Trauma
The best way to deal with traumatic eye injuries is to prevent them in the first place. Here are some practical steps to reduce your risk:
-
Wear protective eyewear during sports or when working in hazardous environments.
-
Use seat belts to reduce the risk of facial injuries in car accidents.
-
Keep sharp objects stored safely at home to avoid accidental injuries.
-
Take extra precautions on slippery surfaces to prevent falls.
-
Educate children about the importance of eye safety in play and daily life.
These simple actions can significantly lower the chances of experiencing eye trauma.
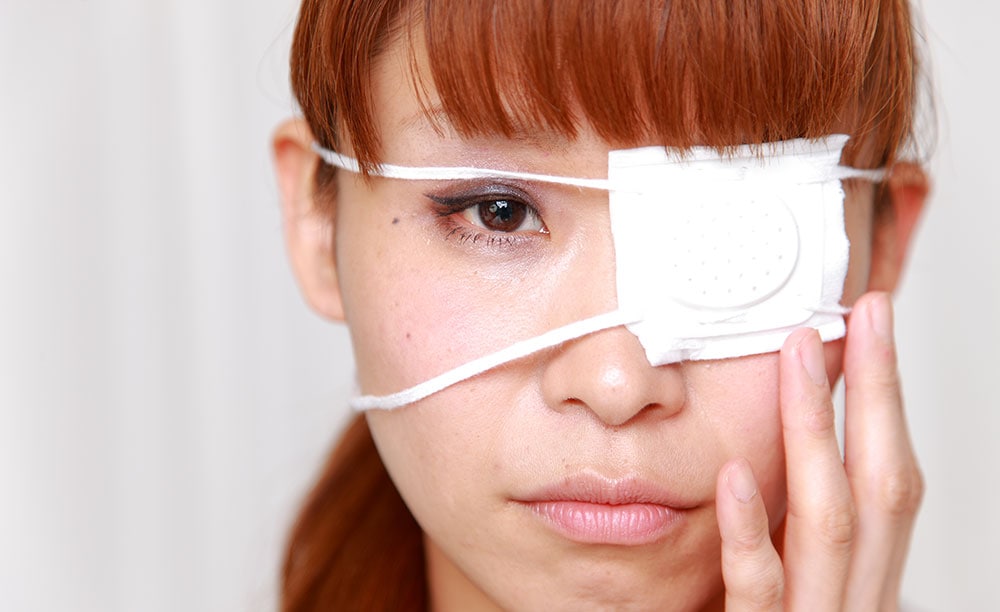
Recovery and Long-Term Outlook
Recovery from a traumatic eye injury depends on its severity. Minor bruises may heal within days, while more complex injuries might require surgery and months of rehabilitation. Regular follow-up with an eye specialist is critical to monitor healing and prevent complications such as infection, scarring, or secondary glaucoma.
Even after recovery, patients are often advised to avoid risky activities until the eye has fully regained strength. In some cases, protective eyewear may be recommended for life, especially if the injury has weakened the natural defenses of the eye.

Final Thoughts
The human eye is both strong and fragile. While it can withstand some pressure and injury, it is not designed to endure high-impact trauma. What may look like a simple bruise could, in reality, be hiding serious internal damage that threatens your vision.
If you or someone you know suffers an eye injury—whether from a fall, a sports accident, or any other cause—never dismiss it as minor. Immediate professional evaluation is the safest path forward. With quick action and proper treatment, many traumatic eye injuries can heal without lasting consequences.
Protecting your vision should always be a top priority. After all, once lost, eyesight is extremely difficult to restore.
