Cannabis Decriminalization Around the World: Benefits, Risks, and the Ongoing Debate
In recent years, more countries have moved toward decriminalizing or legalizing cannabis. This shift reflects evolving perspectives on public health, criminal justice, and economic opportunity. While cannabis is often considered less harmful than alcohol or tobacco, it remains a psychoactive substance with unique effects that require careful consideration.

What Does Cannabis Decriminalization Mean?
Decriminalization generally refers to reducing or removing criminal penalties for the possession or personal use of small amounts of cannabis. Instead of facing arrest or jail time, individuals may receive fines, education programs, or no punishment at all.
Decriminalization differs from legalization:
-
Decriminalization: Personal possession is no longer a criminal offense, but production and sale may remain illegal.
-
Legalization: Cannabis is legally regulated, allowing cultivation, distribution, and sale under government oversight.
Countries Moving Toward Decriminalization and Legalization
Several nations have taken steps to relax cannabis laws in recent years:
-
Canada: Fully legalized recreational cannabis nationwide in 2018, with a regulated industry.
-
Uruguay: Became the first country to legalize recreational cannabis in 2013.
-
Germany: Passed legislation in 2024 allowing regulated recreational cannabis use.
-
Portugal: Decriminalized the possession of all drugs in 2001, focusing on treatment instead of punishment.
-
Thailand: Decriminalized cannabis in 2022, though regulations continue to evolve.
-
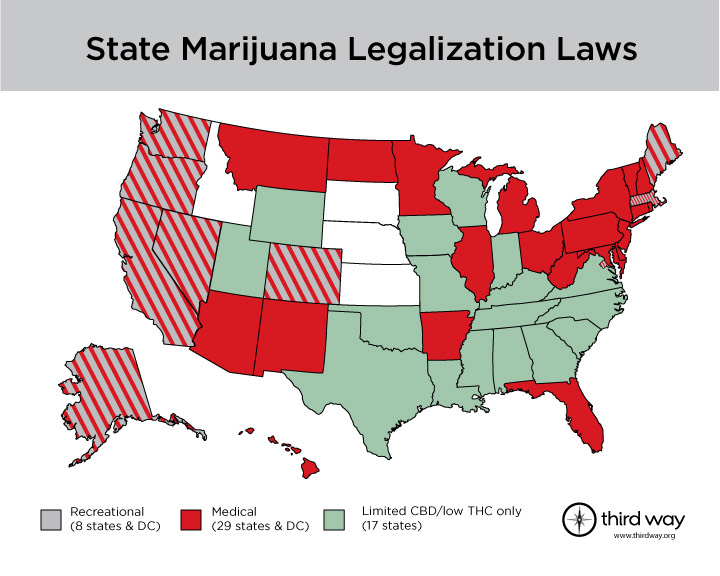
United States: Cannabis remains federally illegal, but over 20 states have legalized recreational use, with many others allowing medical use.
Other countries, including Mexico, South Africa, and Malta, have also moved toward more permissive cannabis laws.
Potential Benefits of Cannabis Decriminalization
Supporters of cannabis reform point to several advantages:
1. Reduced Criminal Justice Burden
Decriminalization helps reduce arrests and incarceration for non-violent offenses, easing the strain on courts and prisons. It also addresses disparities in enforcement, as studies show marginalized communities are disproportionately affected by cannabis-related arrests.
2. Economic Growth
Legal markets generate tax revenue, create jobs, and support ancillary industries such as agriculture, retail, and tourism. For example, legal cannabis sales in the United States reached over $33 billion in 2023 (Statista).
3. Public Health Approach
By treating cannabis use as a health issue rather than a crime, governments can redirect resources toward education, prevention, and treatment programs.
4. Consumer Safety
Legalization allows regulation of cannabis products, including testing for potency and contaminants, reducing risks associated with unregulated markets.
Risks and Concerns Associated with Cannabis
Despite its potential benefits, cannabis use is not risk-free. Health authorities such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) highlight several concerns:
1. Mental Health Effects
High or frequent cannabis use may increase the risk of anxiety, depression, or psychosis in vulnerable individuals. Adolescents and young adults are particularly at risk due to brain development.
2. Impaired Driving
Cannabis can impair reaction time and coordination, increasing the risk of traffic accidents. Public awareness and enforcement remain key challenges.
3. Dependence and Misuse
While cannabis is less addictive than alcohol or nicotine, some users may develop cannabis use disorder, characterized by difficulty controlling use despite negative consequences.
4. Respiratory Risks
Smoking cannabis exposes the lungs to harmful substances. Alternatives such as edibles or vaporizers may reduce this risk, though research is ongoing.
The Importance of Balanced Policy
Effective cannabis policies seek to balance the benefits of decriminalization with strategies to reduce potential harms. Key policy considerations include:
-
Age Restrictions: Limiting access to adults, similar to alcohol or tobacco.
-
Public Education: Providing accurate information on health risks and responsible use.
-
Research Investment: Expanding scientific studies on long-term health effects and potential therapeutic applications.
-
Equity Programs: Ensuring that communities disproportionately impacted by prohibition have opportunities to benefit from the legal market.
Global Public Opinion
Attitudes toward cannabis are shifting worldwide. Polls show increasing support for decriminalization and legalization, particularly among younger generations. However, concerns remain among some policymakers and health experts about normalization, youth use, and long-term public health outcomes.
Conclusion
Cannabis decriminalization is gaining momentum across the globe, reflecting changing social attitudes and recognition of the limitations of prohibition. While cannabis may be less harmful than alcohol in some respects, it is not without risks.
A balanced approach—one that combines legal regulation, public health education, and responsible use guidelines—offers the best path forward. Honest discussion of both the pros and cons ensures that societies can maximize benefits while minimizing potential harms.

